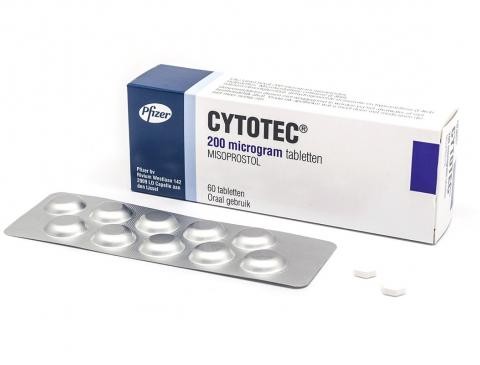
Cytotec - Product Description
Overview:
Cytotec (misoprostol) is a versatile medication primarily known for its role in preventing NSAID-induced gastric ulcers. It is a synthetic prostaglandin E1 analog that mimics the natural protective substances found in the stomach, helping to maintain the stomach lining’s integrity and reduce acid secretion. Beyond its gastrointestinal applications, Cytotec is also widely used in obstetrics and gynecology for its ability to induce labor, manage postpartum hemorrhage, and assist in medical abortion. Cytotec is administered orally, and its dosage and frequency depend on the specific condition being treated.
Indications:
- Prevention of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers: Especially in patients at high risk of gastrointestinal complications.
- Obstetric use: For cervical ripening and labor induction, particularly in cases requiring medical intervention.
- Management of postpartum hemorrhage: To control excessive bleeding following childbirth.
- Medical abortion: In combination with other medications to terminate a pregnancy.
How to Use:
Cytotec is usually taken orally with food to minimize potential gastrointestinal side effects. The dosage varies based on its use:
- For ulcer prevention, the typical dose is 200 mcg four times a day.
- For labor induction, the dose is generally 25 mcg every 4-6 hours, but the regimen may differ based on clinical guidelines and patient conditions.
- For postpartum hemorrhage, higher doses may be administered either orally or sublingually.Always follow the healthcare provider's instructions, and never use Cytotec without medical supervision due to its potent effects and potential risks.
Advantages:
Cytotec offers a wide range of benefits due to its versatility. In gastroenterology, it effectively prevents ulcers in patients taking NSAIDs, significantly reducing the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding and other complications. In obstetric care, it provides a cost-effective, reliable method for inducing labor and managing postpartum hemorrhage, which is particularly valuable in settings with limited access to healthcare. Cytotec's ability to serve multiple functions makes it a critical tool in various clinical scenarios.
Conclusion:
Cytotec is a multifunctional medication with applications in both gastroenterology and obstetrics. Whether preventing NSAID-induced ulcers or assisting in labor and postpartum care, Cytotec offers effective solutions for critical health issues. However, it must be used with caution, and only under medical supervision, due to its powerful effects and potential side effects.
Composition:
Each Cytotec tablet contains 200 mcg of misoprostol, a synthetic prostaglandin E1 analog. Inactive ingredients include hydrogenated castor oil, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium starch glycolate.
Note:
Cytotec is contraindicated in pregnant women who are using it for ulcer prevention due to its uterotonic effects, which can induce labor or cause abortion. Common side effects include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and nausea. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about any pre-existing conditions or concurrent medications to avoid adverse reactions.